
We present a novel approach to fault detection and Physical Asset Health Management (PAHM) called Logical Analysis of Data (LAD). LAD is a supervised learning, artificial intelligence, data mining technique that possesses distinctive advantages which proved to be of use in PAHM. This approach has been introduced by a group of researchers at Rutgers University in the USA, in the medical field, and it was adapted and used in the field of PAHM for the first time by our group of researchers.
(RAMS 2012)
Conferences and Events

In this paper, we propose a multiple fault prognostic methodology which considers the condition monitoring data collected from equipment that experiences one of several different failure modes over its life span. The methodology is based on the exploitation of historical data for knowledge extraction and representation in the form of relevant patterns. Since the technique used is non statistical, none of the usual statistical assumptions, such as the independency of failure modes, are necessary.
(RAMS 2015)

While traditional maintenance cost optimization is based on finding the reliability, and thus the probability of failure over time, in this paper, we show how to exploit condition monitoring data in machining operation in order to extract intelligent knowledge, and use this knowledge to determine the tool replacement time. This work is motivated by the increasing use of sensors in general, and specifically in condition monitoring. We show how the large volume of data that is now available in many industrial sites can give indications to the machining's operator in order to replace the tool. We use a methodology called Logical Analysis of Data (LAD). (RAMS 2015)

In this paper, the conditional reliability function and the Remaining Useful Life (RUL) of a cutting tool are estimated as a function of the current condition's states. RUL is estimated based on the available information obtained from condition monitoring. The cutting forces' measurements define the states, and are considered as the monitoring signals that offer diagnosis of the tool wear state. The cutting tool is used under constant machining parameters, namely the cutting speed, the feed rate, and the depth of cut. Experimental data is collected during turning titanium metal matrix composites (TiMMCs) which are a new generation of materials and have proven to be viable in aerospace application.
(RAMS 2016)
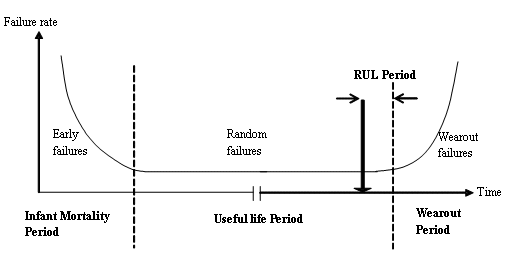
This paper presents a prognostic methodology that can be implemented in a condition-based maintenance (CBM) program. The methodology estimates the remaining useful life (RUL) of a system by using a pattern-based machine learning and knowledge discovery approach called Logical Analysis of Data (LAD). The LAD approach is based on the exploration of the monitored system's database, and the extraction of useful information which describe the physics that characterize its degradation. The diagnostic information, which is updated each time the new data is gathered, is combined with a non-parametric reliability estimation method, in order to predict the RUL of a monitored system working under different operating conditions.
(RAMS 2016)

This paper is aimed at presenting a new approach, for new items classification that takes into consideration multiple criteria. The proposed approach is a data mining technique called Logical Analysis of Data (LAD). LAD is based on Boolean theory that is used for pattern recognition. For this study a Multi-class LAD model is used to support ABC items’ classification process based on multiple criteria. Two applications for two different datasets are presented.
(ISERC 2016)

This paper proposes a risk identification and estimation process based on the Logical Analysis of Data (LAD) concerning machinery-related accidents. An optimization combinatorial data mining algorithm based on Boolean logic, LAD generates patterns which are interactions of accident-related causes that characterize and distinguish accident events. The paper presents the LAD approach as applied to machinery risk management in different contexts of use.
(ISERC 2016)

In this paper, we are finding the tool replacement time when a tool is used under constant machining conditions, namely the cutting speed, the feed rate, and the depth of cut, during turning titanium metal matrix composites (TiMMCs). Despite being expensive, MMCs are a new generation of materials which have proven to be viable in various fields such as biomedical and aerospace industrial. Proportional Hazard Model (PHM) is used to model the tool’s reliability and hazard functions using Exakt software.
(ISERC 2014)
